Introduction to Eczema and Diet
Understanding Eczema: The Basics
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It’s often seen in children but can occur at any age. A significant number of children with eczema also have food allergies. The relationship between eczema and food allergies can greatly impact the quality of life for those affected, leading to an ongoing search for relief through dietary changes. However, it is important to note that food is just one of the many triggers that can exacerbate eczema symptoms, and the relationship between diet and eczema is complex.
Before making any dietary changes, it is essential to consult with a doctor, especially when food allergies are present. Safe dietary modifications can be an integral part of managing eczema, but they should not replace other treatments prescribed by a healthcare provider. Additionally, an evidence-based approach is necessary because nutritional needs vary from person to person.
How Food Can Impact Eczema
If you are dealing with eczema, being observant about the foods you eat may reveal potential triggers for your symptoms. Identifying and eliminating potential dietary triggers is often a process of trial and error. Here are some pertinent questions that you might consider:
– Do your eczema symptoms get better while avoiding a particular food? Monitoring any improvements while excluding specific foods from your diet can help pinpoint possible allergens or irritants. However, it is crucial to note that if your symptoms do not improve after eliminating a food, it may not be necessary to continue avoiding it.
– Do your eczema symptoms come back after reintroducing a food? If you notice that symptoms worsen after adding a specific food back into your diet, this may be an indicator that you should consider limiting or avoiding that food altogether.
Other tips for managing eczema through diet include keeping a food diary to log what you eat and any symptoms that occur, which can help you and your doctor identify patterns and make informed decisions about your diet. Stay hydrated, as water is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids that can support skin health, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. Foods high in antioxidants, like fresh fruits and vegetables, may also help reduce inflammation.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all eczema diet; what may be effective for one person might not work for another. Dietary changes should be personalized and made in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure all nutritional needs are met while managing eczema symptoms effectively.
Keep in mind that while the role of diet in managing eczema is increasingly recognized, it is one part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Always consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet, especially when dealing with a complex condition like eczema.
The Common Culprits: Foods That May Worsen Eczema
Identifying Eczema’s Dietary Triggers
A vital part of managing and understanding eczema involves identifying potential triggers, especially in your diet. You may have noticed certain foods exacerbating your skin condition, leading to considerable discomfort. It’s imperative to pay close attention to your body’s response after consuming specific foods. If you detect a correlation between the worsening of eczemous symptoms and certain dietary choices, it’s possible that you’re dealing with a food-triggered eczema flare-up.
Let’s explore how you can effectively monitor dietary influences on your eczema. Begin by eliminating the suspected food from your diet for a period and observe any changes in your symptoms. Should you notice an improvement in your eczema, it may indicate that the eliminated food could be a trigger. On the other hand, if there is no change in your symptoms, the food in question might not be a contributing factor, and you may not need to exclude it from your diet.
However, the true test occurs when you reintroduce the food. If upon its reintroduction your symptoms flare up again, this might be a sign that the food indeed contributes to your eczema. In such cases, considering avoidance of the trigger food might be beneficial for your skin health. It is essential to approach this elimination diet methodically and preferably with the guidance of a healthcare provider or a dietitian, as it can be complex and may require professional input to ensure balanced nutrition.
Common Foods Known to Cause Eczema Flare-Ups
Certain foods are notorious for triggering eczema in susceptible individuals. These often include nuts, milk, and wheat, which have been associated with the release of inflammatory T cells and immunoglobulin-E, elements that contribute to allergic reactions and inflammations. Additionally, there are other common culprits, such as eggs, dairy products, soy, citrus fruits, tomatoes, gluten, and specific spices like cloves, cinnamon, and vanilla. These foods can provoke an eczema response in some people, causing discomfort and exacerbating the condition.
For those dealing with dyshidrotic eczema, a type of eczema that affects the hands and feet, it’s also important to be aware of foods containing nickel, as this can aggravate symptoms. Foods high in nickel include beans, black tea, canned meats, chocolate, and certain nuts and seeds.
It’s crucial to recognize that the response to these foods can be highly individual. While some may experience severe reactions, others might not have any noticeable impact. Therefore, the process of identifying and managing dietary triggers is deeply personal and may entail a trial-and-error approach.
Determining the effects of specific foods on your eczema involves diligent observation and patience. With careful monitoring and, where necessary, the guidance of health professionals, you can identify potential food triggers and make informed decisions about your diet, hopefully leading to better management of your eczema symptoms.
The Trouble with Eggs and Dairy

The Connection between Eczema and Eggs
As someone managing eczema, it’s important for you to understand how your diet influences your condition. Eggs, a common staple in many diets, may be one of the items to reconsider. Eggs have been identified as one of the typical eczema triggers due to the presence of certain proteins that can provoke an allergic response, resulting in increased inflammation and eczema flare-ups. If you notice a pattern of symptoms after consuming eggs, consider eliminating them from your diet for a trial period to see if your condition improves.
When reintroducing eggs, do so gradually and take note of any changes in your eczema. Should you observe redness, itchiness, or any other familiar eczema symptoms returning with the reintroduction, it is quite possible that eggs are not suitable for your condition. Paying strict attention to these signs will aid you in ruling out or confirming eggs as an eczema trigger. If it turns out they are problematic, it would be prudent for you to find alternative sources of protein and nutrients to replace the nutritional benefits provided by eggs.
Dairy Products and Eczema Symptoms
Similarly to eggs, dairy products are commonly implicated in exacerbating eczema symptoms. This is because the proteins found in cow’s milk and other dairy items can sometimes cause an immune system reaction that leads to skin inflammation. Moreover, for certain individuals, lactose intolerance or a sensitivity to the sugars found in dairy products can contribute to eczema attacks.
If you suspect dairy may be affecting your eczema, try eliminating these products from your diet temporarily to monitor any improvements. Common dairy products to avoid include milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. In the absence of dairy, ensure you are receiving adequate calcium and vitamin D from other sources to maintain bone health and overall wellness.
It’s advisable to reintroduce dairy into your diet slowly, just like with any other potential eczema trigger. Take careful note of how your skin responds during this period. If symptoms return, you may need to consider dairy alternatives like plant-based milks and non-dairy cheeses, which can offer similar tastes and textures without the inflammatory effects associated with traditional dairy products.
It’s also valuable to note that fermented dairy products like kefir or certain types of yogurt might be better tolerated, as they contain probiotics which can support gut health and potentially improve eczema. However, this can be very individual, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Navigating the dietary landscape with eczema can be challenging, but with methodical trial and observation, you can develop a more eczema-friendly diet. Consulting with healthcare professionals, especially those specializing in allergy and immunology, can provide you with personalized advice and support. This collaborative approach can help manage your eczema effectively while ensuring your diet remains balanced and nutritious.
Soy and Citrus: Potential Eczema Offenders

The Role of Soy in Eczema
When considering dietary factors that might aggravate your eczema, you shouldn’t overlook soy. This plant-based protein source is prevalent in various forms, including soybeans, soy milk, tofu, and many processed foods. Soy contains several allergens and is known to be one of the more common food sensitivities that could trigger an eczema outbreak. The allergenic components in soy are proteins that can elicit an allergic reaction leading to the release of histamines, which can worsen inflammation and exacerbate eczema symptoms.
If you suspect soy might be contributing to your eczema flare-ups, you might want to eliminate it from your diet for a period and observe any changes. Should you choose to reintroduce soy, it’s essential to do it gradually and monitor any reactions. If your skin condition worsens after eating soy, it’s likely best to minimize or avoid it altogether. Additionally, when eliminating soy, ensure you replace it with other nutritious foods to maintain a balanced diet. Seek out alternative sources of protein, such as lean meats, fish, eggs (if they do not trigger your eczema), and other legumes which may be more eczema-friendly for your specific condition.
Why Citrus Fruits Might Trigger Eczema
Much like other foods, citrus fruits — such as oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits — can potentially lead to eczema flare-ups in some individuals. The high acidity and vitamin C content in citruses are believed to stimulate histamine release in the body which can exacerbate inflammation and eczema symptoms. Moreover, the skin and peels of citrus fruits contain compounds that can irritate sensitive skin when handled or consumed, potentially leading to contact dermatitis in addition to systemic reactions.
If you notice a correlation between your eczema symptoms and citrus intake, you may want to consider reducing or cutting out these fruits from your diet temporarily to assess their impact. However, vitamin C is an essential nutrient, so you should ensure that you receive adequate amounts from other less allergenic sources, such as green leafy vegetables or non-citrus fruits like kiwis and strawberries, if you choose to avoid citrus.
Monitoring and reintroducing citrus fruits into your diet can help you pinpoint whether they are a trigger for your eczema. Stay observant of your skin’s reaction when you eat citrus and speak to a dietitian or allergist for tailored advice. You should also maintain a well-rounded diet to support your overall health while you navigate through potential eczema triggers.
Managing eczema often requires a personalized strategy where diet plays a crucial role. It’s essential to understand your triggers and listen to your body’s responses to create an effective management plan. While navigating these dietary restrictions can be frustrating, support is available. Work closely with your healthcare team to ensure you’re not only managing your eczema but also meeting all your nutritional needs for a healthy, well-balanced life.
Tomatoes, Gluten, and Eczema
Tomatoes as a Hidden Eczema Trigger
You might find tomatoes to be a delicious addition to salads, sandwiches, and sauces, but for those with eczema, they could be causing more harm than flavor. Tomatoes, along with citrus fruits, contain certain compounds that may provoke an immune response, leading to skin irritation and eczema flare-ups. If your eczema coincides with consuming these foods, it may be worth considering their role in your diet.
To determine if tomatoes are contributing to your eczema symptoms, you might try an elimination diet. This means cutting tomatoes and tomato-based products out of your meal plan for a few weeks and observing any changes in your skin condition. If you see an improvement, you may have uncovered a trigger. However, it’s important to reintroduce them slowly to confirm your suspicions, as entirely avoiding them can lead to missing out on vital nutrients like vitamin C and potassium. If you discover that tomatoes are an issue, there are alternative sources of these nutrients, such as leafy greens and other vegetables.
How Gluten Can Affect Eczema
Gluten is another dietary component that can be troublesome for individuals with eczema, particularly those with a sensitivity or celiac disease. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, might cause inflammation in certain individuals, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms. If you suspect gluten is influencing your eczema, it can be beneficial to undergo testing for celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity with the assistance of a healthcare provider.
Similar to other elimination trials, removing gluten from your diet should be done judiciously and only if there is a well-founded suspicion that it’s causing issues with your eczema. Look for improvements in your skin while you avoid gluten and use alternative grains such as quinoa, rice, and corn to ensure you’re maintaining a well-rounded diet. Keep in mind that gluten is a common ingredient in many processed foods, so careful reading of labels is paramount during this process.
Upon noticing an improvement without gluten, reintroduce it gradually while monitoring your eczema symptoms closely. If your skin reacts negatively upon reintroduction, you may need to adapt to a gluten-free lifestyle. Fortunately, the market for gluten-free products has expanded significantly, offering a variety of alternatives that can help you maintain a diverse and satisfying diet.
In any dietary modifications for eczema, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet. Eliminating entire food groups without proper substitution can lead to nutrient deficiencies. Work with a dietitian or nutritionist who can help you find safe and nutritious alternatives to maintain your health. Moreover, ongoing communication with your healthcare team will ensure a holistic approach to managing your eczema, integrating dietary strategies with medical treatments to find relief and promote skin health.
Spices That May Aggravate Eczema

Beware of Specific Spices: Cloves, Cinnamon, and Vanilla
While spices like cloves, cinnamon, and vanilla are beloved for their aromatic and flavor-enhancing qualities, you may need to consider the potential impact they can have on your eczema. These spices contain compounds that can trigger an allergic response in some individuals, potentially worsening eczema symptoms. If you have noticed a pattern of eczema flare-ups after consuming dishes with these spices, it could be worth investigating whether they are contributing to your skin irritation.
To assess your sensitivity to these spices, approach your diet with caution. Try eliminating cloves, cinnamon, and vanilla from your meals for several weeks to monitor any changes in your eczema symptoms. Remember, even small amounts of these spices in your food can be sufficient to cause a reaction if you are sensitive to them. During this period of elimination, take note of any reduction in redness, itching, or inflammation.
After the trial, reintroduce each spice one at a time into your diet to determine if any specific one is a trigger for your eczema. It’s essential to keep all other dietary and lifestyle factors constant during this phase to ensure accurate results. If you experience a resurgence of symptoms, it may be time to consider eliminating that particular spice from your diet long-term. But before taking any drastic dietary measures, consult with a healthcare professional to aid in your investigation and ensure that you are not missing out on key elements of a varied and nutritious diet.
Identifying Spice Sensitivities and Eczema
Identifying spice sensitivities may require a meticulous and patient approach. The relationship between food sensitivities and eczema can be complex and highly individual. To start, maintain a detailed food diary where you record everything you consume, making particular note of meals that include these spices. This diary can help you and your healthcare provider identify patterns and possible links between your diet and eczema flare-ups.
Once you have successfully identified a spice that seems to trigger your eczema, it does not mean you have to give up on flavor. Many herbs and spices may not cause the same inflammatory response and can safely be used to season your dishes. It may also be beneficial to undergo allergy testing. A healthcare provider can perform specific tests to determine if you have a true spice allergy, which can guide you in making more informed dietary choices.
Remember that managing eczema often requires a multi-faceted approach. In addition to dietary adjustments, you should also consider other lifestyle changes that may improve your skin condition, such as stress management techniques, regular moisturizing, and avoiding harsh soaps and chemicals. Always discuss changes to your diet or eczema management plan with a professional to ensure that you are taking steps that positively contribute to your overall health and well-being.
Eczema and the Nickel Connection
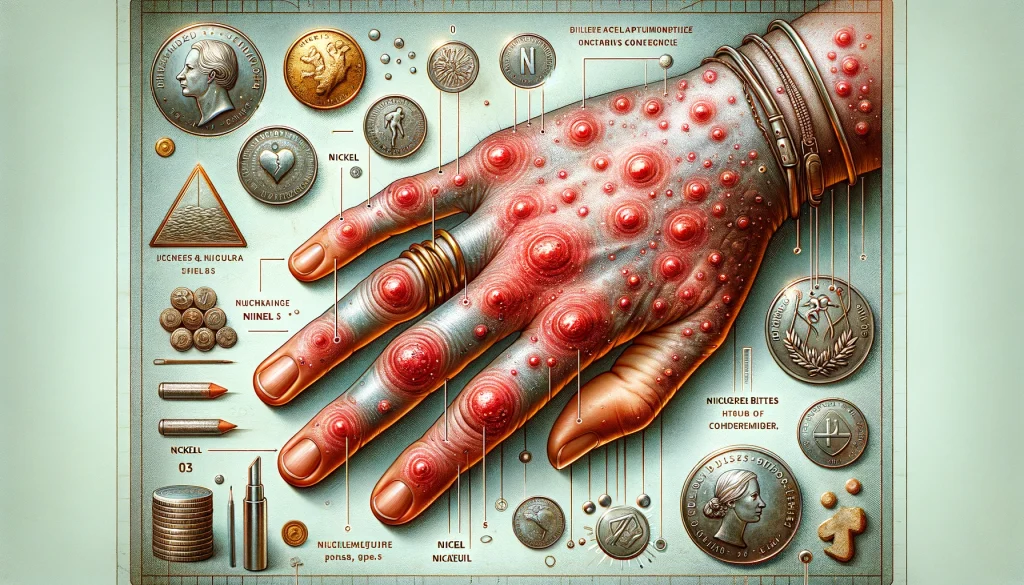
Understanding Dyshidrotic Eczema and Nickel
If you have been experiencing persistent eczema flare-ups, particularly on your hands and feet, it may be beneficial for you to explore the possibility of a nickel allergy. Nickel allergy is widespread and can result in allergic contact dermatitis, where the skin responds to contact with nickel-containing items, leading to redness, itching, and even blisters – symptoms synonymous with eczema. Everyday objects like jewelry, electronics, buttons, and zippers are often culprits. It’s not just about what you touch; certain foods can also be high in nickel, thus potentially exacerbating a condition known as dyshidrotic eczema.
Being mindful of the objects you come into contact with and what you consume is important when you have eczema. If you’re noticing a correlation between your flare-ups and exposure to metal items, it might be time to consult with your healthcare provider. They can conduct a simple patch test to verify if you indeed have a nickel allergy. Understanding your triggers is a significant first step towards managing your symptoms more effectively.
Low Nickel Diet: Is It Worth a Try for Eczema Relief?
Implementing a low nickel diet might seem daunting at first, but it could potentially bring you the relief you’ve been seeking from your eczema symptoms. Foods that are typically high in nickel include canned foods, whole grains, chocolate, nuts, seeds, soy products, and even certain fruits and vegetables. As with other elimination diets, the goal here is to identify and remove the triggers that aggravate your condition.
Starting a low nickel diet isn’t a decision to be made lightly or on an impulse. It requires careful planning to ensure you are not inadvertently depriving your body of essential nutrients. The approach is to systematically eliminate high-nickel foods from your diet, monitor the response of your eczema, and then, if there’s an improvement, methodically reintroduce them one at a time. This process helps pinpoint the dietary sources that might be contributing to your symptoms.
It is imperative to remember that changes in diet should be made with the guidance and support of healthcare professionals, such as your doctor or a registered dietitian. This is to prevent nutritional deficiencies and to ensure that the diet you’re following is both suitable for your eczema management and supportive of your overall health.
In the event you decide to try out a low nickel diet, you’ll have to become vigilant about reading food labels and asking about ingredients when eating out. The prevalence of nickel in foods can make avoidance challenging, but it’s not insurmountable. With the right guidance, you’ll learn to identify safe foods and make substitutions that align with the nutritional demands of your body, all while potentially keeping your eczema in check. Remember, your journey with eczema is personal and unique, and what works for one person might not work for another. It’s essential to track your symptoms and discuss your diet with your healthcare provider to ensure you’re on the right track toward managing your eczema effectively.
Beyond Diet: Recognizing Other Eczema Triggers
The Impact of a Weakened Immune System on Eczema
As you navigate the complexities of managing your eczema, it’s important to understand that dietary adjustments may not address all aspects of the condition. The immune system plays a central role in the inflammation that characterizes eczema. When your immune system is weakened—whether due to stress, illness, or fatigue—it may be less effective at regulating inflammatory responses, potentially leading to increased eczema symptoms.
You should be aware of situations that may compromise your immune functions, such as lack of sleep, chronic stress, and exposure to illness. Ensuring a well-balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals, can support immune health. Additionally, practices like regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques can bolster your immunity and may help to keep eczema under better control. Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss ways of supporting your immune system as part of a comprehensive approach to managing eczema.
Non-Food Factors Contributing to Eczema Flare-Ups
Aside from your diet and immune health, there are numerous other factors that might be contributing to your eczema. Environmental allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and molds can be common triggers for many people. It’s worthwhile to have allergy tests performed to identify potential environmental allergens that may be affecting your condition. Once identified, taking steps to minimize exposure to these allergens can be beneficial.
Skin irritants, ranging from soaps and detergents to fabrics and skincare products, can also provoke flare-ups. Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products whenever possible, and dress in soft, breathable materials to avoid irritation to the skin.
The climate and changes in weather can also play a role. Some individuals find that their eczema worsens with dry, cold air, while others may be more affected by hot, humid conditions. Using a humidifier in winter and seeking air-conditioned environments during hot weather can help mitigate these effects.
Moreover, your mental well-being may impact your eczema. High levels of stress and emotional turmoil can lead to exacerbated skin conditions. If you suspect a link between your mental health and eczema, consider techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or speaking with a mental health professional. These approaches not only help in managing stress but may also have a positive effect on your skin health.
In summary, while diet plays a role in the management of eczema, it’s crucial to consider the full scope of potential triggers. By addressing factors such as immune health, environmental allergens, skin irritants, climate, and emotional well-being, you may find greater success in managing your condition. Remember, each individual’s triggers can be very different, and therefore, a personalized strategy developed with the assistance of your healthcare provider is paramount for effective eczema control.
Developing Your Personal Eczema Diet Plan
How to Identify Your Specific Food Irritants
Understanding your unique dietary triggers is a critical aspect of managing eczema. While every individual’s reaction to food can vary, identifying what exacerbates your symptoms is a personalized process. To begin with, you may want to keep a detailed food diary, meticulously recording everything you eat and drink, along with the timing of your eczema flare-ups. By reviewing your entries over time, you may start to see patterns emerge, indicating which foods might be associated with worsening symptoms.
Consultation with a healthcare provider can facilitate this discovery process. Your doctor can recommend an elimination diet, where you systematically remove potential trigger foods from your meal plan and reintroduce them one by one, watching for changes in your eczema. Skin prick tests or blood tests for IgE antibodies might also be suggested to rule out or confirm food allergies. A qualified dietitian can provide valuable support by helping you to maintain a balanced diet during this period, ensuring that you do not miss out on vital nutrients.
Crafting an Eczema-Friendly Diet: Tips and Tricks
Once you have a better idea of which foods may be causing issues, you can start to craft a diet that supports your skin health while also being enjoyable and nutritionally complete. The foundation of an eczema-friendly diet is often rich in whole foods, abundant in fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Here are some tips to help you build your personalized diet:
Avoid processed and sugary foods as these can increase inflammation in the body, potentially leading to more frequent or severe flare-ups.
Hydrate consistently, as well-moisturized skin can be less prone to eczema symptoms. Drinking plenty of water and maintaining a diet with hydrating foods, like cucumbers and watermelon, can be beneficial.
Incorporate probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt and kefir into your diet. These foods promote a healthy gut, which is linked to a stronger immune system and possibly improved skin health.
Ensure you get enough vitamin D, which can come from sun exposure, fortified foods, and supplements as recommended by your healthcare provider. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with more severe eczema symptoms.
During this journey, it’s desirable to be flexible and patient with yourself. Changes in your diet can take time to show results on your skin, and it’s not uncommon to experience setbacks. Partner with healthcare practitioners you trust, be methodical in your approach to change, and consider each step an opportunity to better understand your body and the impact of nutrition on your eczema. Remember, the goal is not to find a quick fix but to establish a sustainable, balanced dietary routine that supports your well-being and manages your eczema symptoms effectively.
Your Guide to Uncovering Food Triggers and Managing Eczema
Understanding Eczema and Diet Interactions
If you are grappling with eczema, you might find that certain foods can either aggravate or alleviate your condition. It’s essential to understand how diet can impact eczema to create a tailored plan that suits your specific needs. Be vigilant about noting any foods that trigger inflammation in your body, as this may translate to an eczema flare-up.
Strategies for Identifying Food Sensitivities
Navigating the complex relationship between your diet and eczema involves becoming an expert observer of your body’s responses. Consider conducting an elimination diet under the supervision of a healthcare provider, methodically removing suspect foods and monitoring your skin’s reaction. Remember, the primary goal here is to zero in on foods that trigger your symptoms, not to limit your nutrition unnecessarily.
During this investigative phase, keep a detailed food diary. Document everything you consume and note how your skin feels daily. Over time, correlations between certain foods and eczema flares may become more apparent, guiding you to make informed choices about your diet.
Formulating an Eczema-Supportive Eating Regimen
Once you identify possible culprits, focus on devising a meal plan that reinforces your skin health without feeling overly restrictive. Opt for foods known for their anti-inflammatory properties, such as colorful fruits, green leafy vegetables, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids like flaxseeds, walnuts, and fatty fish.
It’s equally important to maintain hydration. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day and integrate moisture-rich foods into your meals. This can have a positive effect on your skin’s hydration levels, potentially reducing eczema symptoms.
Additionally, foster a healthy gut environment by including probiotics in your diet. The link between a robust gut microbiome and improved immune function has been established, and it may also play a role in managing eczema. Foods such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can be excellent sources of probiotics.
Securing sufficient vitamin D is another vital aspect of supporting skin health. Whether through safe sun exposure, vitamin D-rich foods, or supplements, adequate levels of this nutrient can make a significant difference in the severity of eczema symptoms.
Building Your Support System
Embarking on this dietary exploration for eczema management is a step towards self-empowerment, but it doesn’t have to be a solitary journey. Enlist the support of healthcare professionals, including dietitians, dermatologists, and allergists who can guide you with expertise and compassion. These alliances are invaluable, providing structure and knowledge to help you achieve the best possible outcomes.
Above all, be patient and kind to yourself through this process. Finding the right dietary balance for eczema relief is a gradual and personal endeavor. Give yourself grace to adjust and learn from each situation, understanding that each step is a stride towards better skin health and overall wellbeing.